
Image 1a. Image of a mouse zygote.

Image 1b. Image of a mouse zygote ready to be microinjected.

Image 2. Mouse blastocyst injected with modified mouse embryonic stem cells.

Image 4A. Image of a 6.5 day post coital embryo (6.5 dpc) in a microinjection session with Cre-recombinase.

Image 3B. Detail of the injection site of a 6.5-day post-coital embryo (6.5 dpc) in a microinjection session with Cre-recombinase.

Image 4A. Mouse sperm detail.

Image 4B. Mouse oocyte In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
The vast majority of these
sperm will disappear when we isolate the oocyte for culture.
Only one will reach the goal.
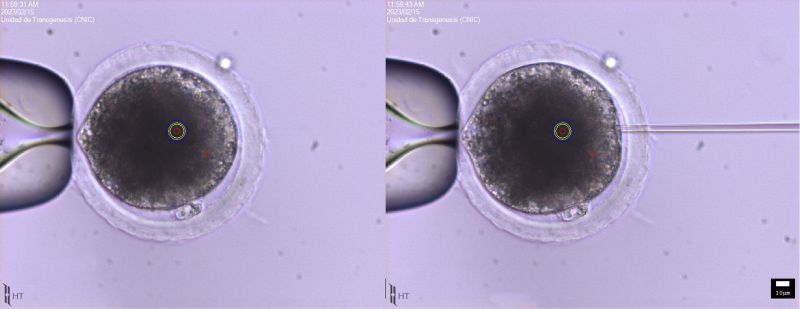
Foto 5. Pig oocytes undergoing microinjection.
Note the high lipid content which obscures the cytoplasm
and hinders the observation of the cytoplasmic content.
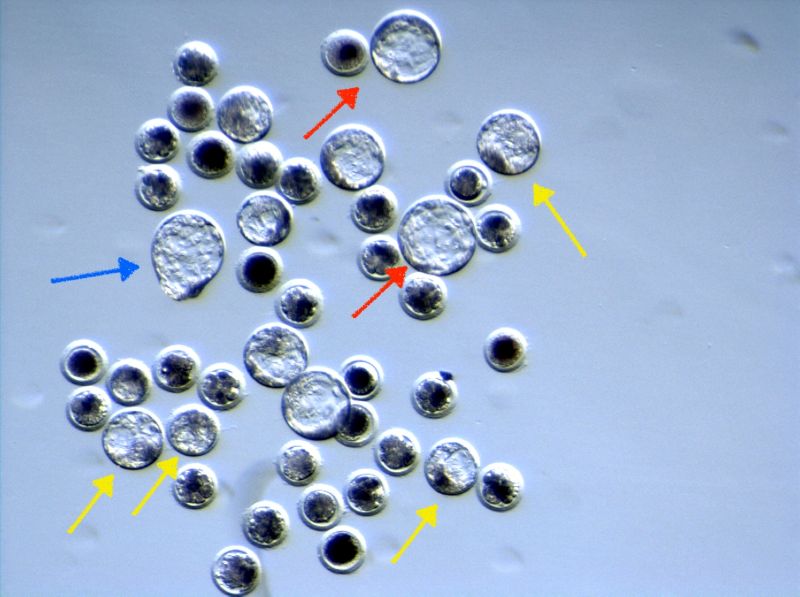
Foto 6. Set of pig embryos in a microinjection experiment with CrispR-Cas9, after 5 days of culture.
Different embryos can be observed at the blastocyst stage, some of them early (yellow arrows),
others expanding (red arrows) and even emerging from the zona pellucida
(time prior to implantation, blue arrow).
Video 1. Sequence of a pronuclear microinjection session in mouse
zygotes.
Video 2. Sequence of a microinjection session of mouse blastocysts
with embryonic stem cells.
Video 3. Sequence of a mouse Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
session.






