Jama Cardiology: An international team identifies the mutations that cause the most frequent congenital heart defects
A multicenter study published in JAMA Cardiology and co-led by scientists at Hadassah Medical Center, Sheba Medical Center, and the CNIC could help in the design of future pharmacological treatments for bicuspid aortic valve
Bicuspid aortic valve is the most common congenital defect in humans, affecting between 1% and 2% of the population. Instead of the usual three symmetric leaflets, affected individuals have two asymmetric valve leaflets. This defect is a frequent cause of aortic stenosis and endocarditis and is associated with early calcification of the aortic valve. Currently the only effective treatment is valve replacement surgery.
But this situation could be changed by the results of a new study published by an international team co-led by Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares group leader Dr. José Luis de la Pompa.
This innovative multicenter study, published in JAMA Cardiology,, reveals that biscuspid aortic valve is cause by mutations in the MINDBOMB1 gene (MIB1), some of them described for the first time in the new study and others previously reported by the same group in an earlier article in Nature Medicine.
Dr. de la Pompa hopes that these discoveries will have a significant impact, helping in the future design of pharmacological treatments as an alternative to valve replacement surgery. “This is an especially exciting prospect because bicuspid aortic valve is the most frequent congentital defect. I addition to helping patients, alternatives to surgery could reduce the cost burden on health care systems,” said Dr. de la Pompa.
For the study, the CNIC team partnered with, among other centers, Hospital Hadassah and Hospital Sheba in Israel, Georges Pompidou European Hospital and the University of Paris in France, the University of Antwerp in Belgium, (Bélgica), Radboud University Medical Center in The Netherlands, Harvard University Medical School in the USA, and the Karolinska Institute in Sweden.
The study combined genome sequencing, the sequencing of candidate genes in a familial cohort, analysis of the association of rare variants in additional cohorts, and further analysis of the association of common variants in a third, large cohort, explained Idit Tessler of Sheba Hospital, a co-leader on the study. The analysis of mutations in patients from different populations strengthens the validity of the study.
To analyze the specific mechanisms through which MIB1 ensures correct heart development, Dr. Rebeca Piñeiro-Sabarís from the team at CNIC, led by Dr. José Luis de la Pompa and co-first author of the study, used CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to introduce the identified mutations into the sensitized genome of mice carrying one mutant allele for the NOTCH receptor. Both mutations (double heterozygosis) were required for the mice to develop bicuspid aortic valve at a high rate, contrasting with the development of the heart defect in human patients with a single mutation in one MIB1 allele (single heterozygotes). The mice carrying both mutations also had defects in the interventricular septum.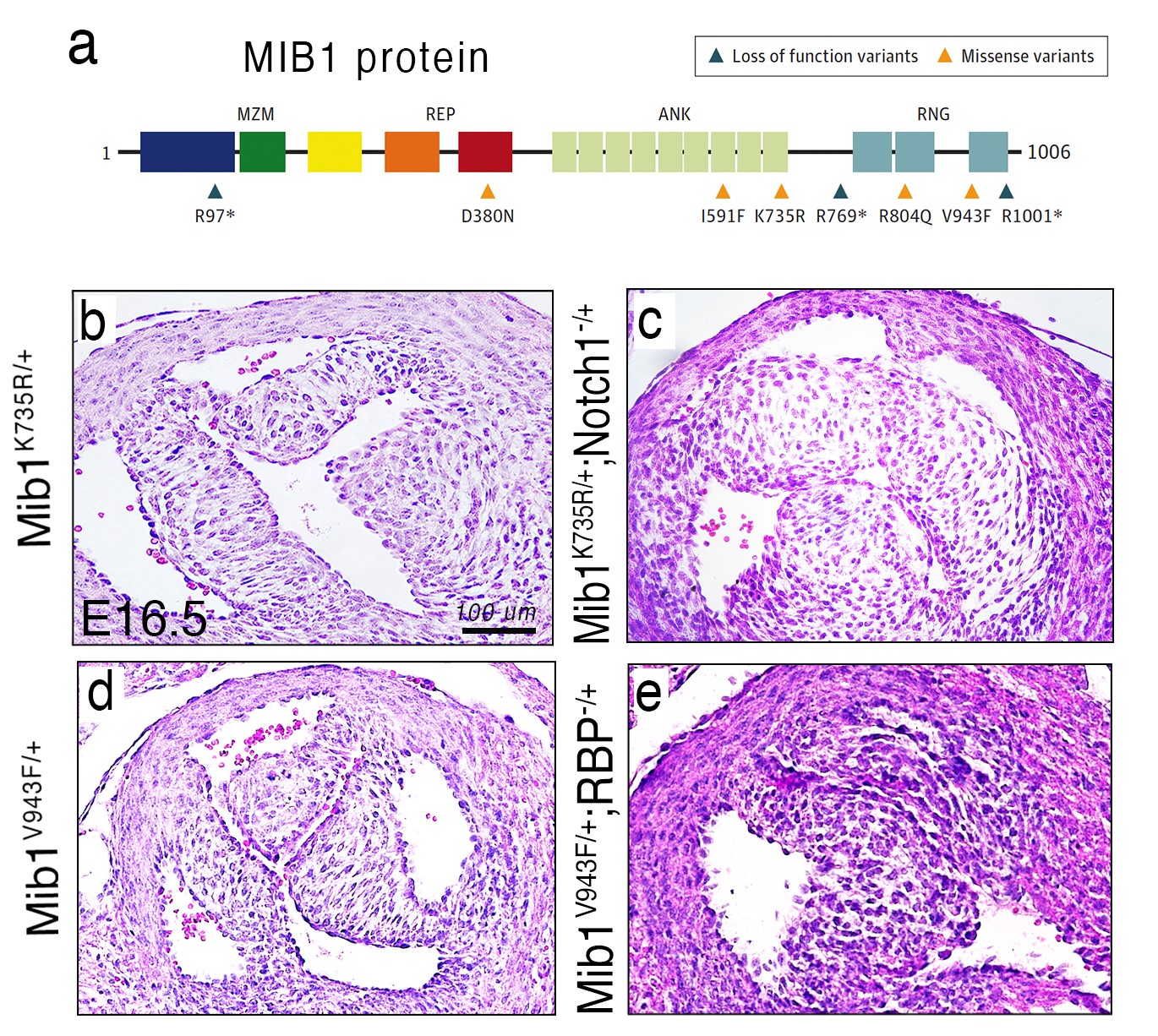
This study is part of Dr. Rebeca Piñeiro-Sabarís' doctoral thesis.
The researchers conclude that the identified association between MIB1 and bicuspid aortic valve highlights the important role of the NOTCH signaling pathway in this congenital defect and the potential of NOTCH pathway components as targets for the design of new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
The study was funded by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (MICIN).











