News search
|
Research 1 Feb 2024 A study published in Nature Cardiovascular Research reveals smooth muscle-derived cells as a new target for reducing the size of atherosclerotic plaque. The results open up new avenues for the design of treatments to enhance the beneficial effect of cholesterol-lowering drugs |
|
Research 23 Jan 2024 The most potent genetic risk factor for Alzheimer disease, APOE4, is associated with an elevated risk of developing subclinical atherosclerosis in middle age, whereas the Alzheimer-protective variant of the same gene, APOE2, protects against subclinical atherosclerosis |
|
Research 19 Jan 2024 A team led by scientists from the CNIC and CNIO has identified a potential therapeutic target that protects the heart in patients with pulmonary hypertension |
|
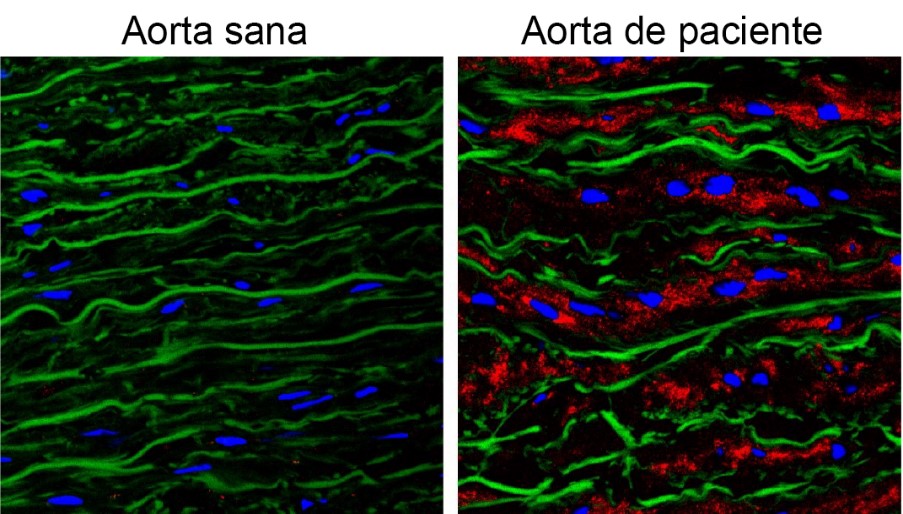
Research 3 Jan 2024 A team led by scientists at the CNIC and CSIC has found that accumulation of versican in the aortas of Marfan syndrome patients triggers the activation of the nitric oxide pathway through the activation of the the protein AKT |
|
About the CNIC 2 Jan 2024 Juan Pedro Bolaños is Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Salamanca. |
|
Research 21 Dec 2023 Johns Hopkins UniversityBloomberg School of Public HealthBaltimore |
|
About the CNIC 19 Dec 2023 Dr. Carla Rothlin is Dorys McConnell Duberg Professor of Immunobiology and Professor of Pharmacology at the Yale School of Medicine, and co-leader of the Cancer Immunology Programme at Yale Cancer Centre. She studied biochemistry and pharmacology at the University of Buenos Aires, where she also undertook her postgraduate research under the direction of Dr. Ana Belén Elgoyhen, focussing on nicotinic receptors expressed in the inner ear. Later, she completed her doctorate and moved to San Diego to join Dr. Greg Lemke’s laboratory at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies. In 2009, Dr. Rothlin was named Assistant Professor in Immunobiology at Yale Medical School |
- ‹ previous
- 8 of 53
- next ›