News search
|
Research 24 May 2023 A study by CNIC researchers published in Nature has found that the omega-6 fatty acid gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), present in breast milk, plays an essential role in ensuring the proper functioning of the heart after birth |
|
Research 21 May 2023 The team led by Dr. Pablo García-Pavía, based at the CNIC and Hospital Puerta de Hierro, has published the first study of a drug able to remove amyloid deposits from the heart |
|
Research 6 Mar 2023 A study could change management of patients who are not critically ill |
|
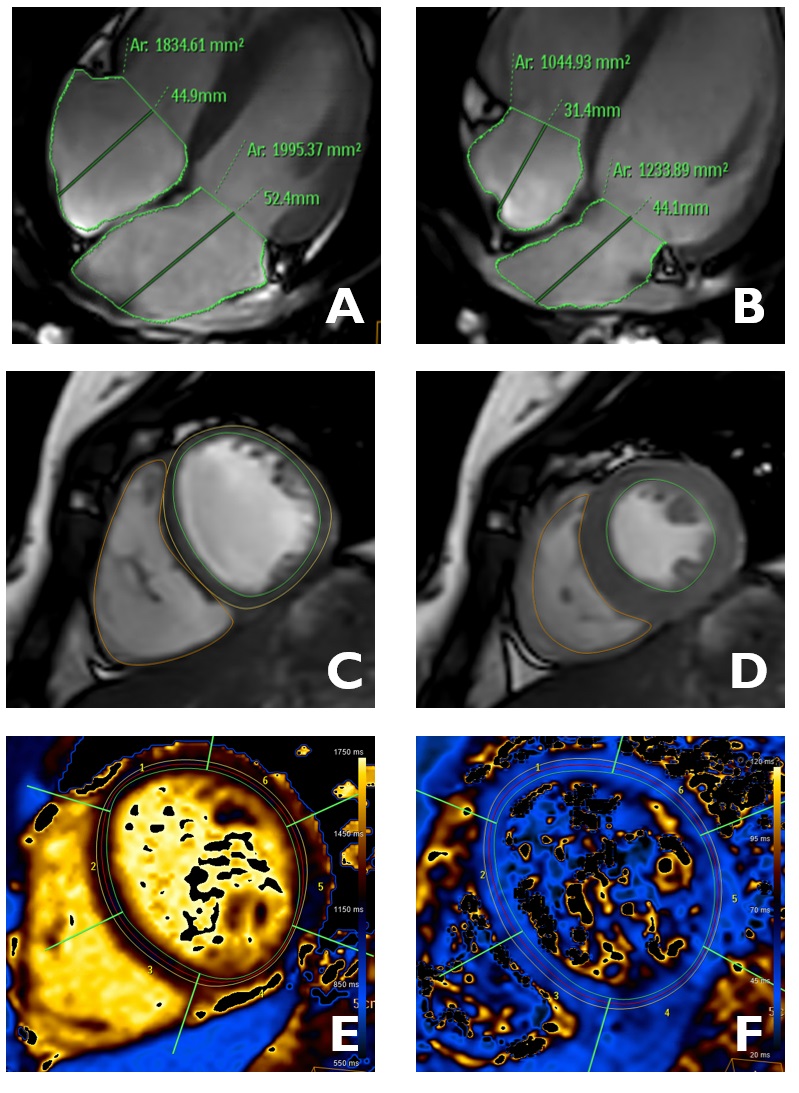
Research 3 Mar 2023 The results, published in eClinicalMedicine, have direct implications for clinical practice by providing a list of reference values for a multitude of cardiac parameters used in daily practice |
|
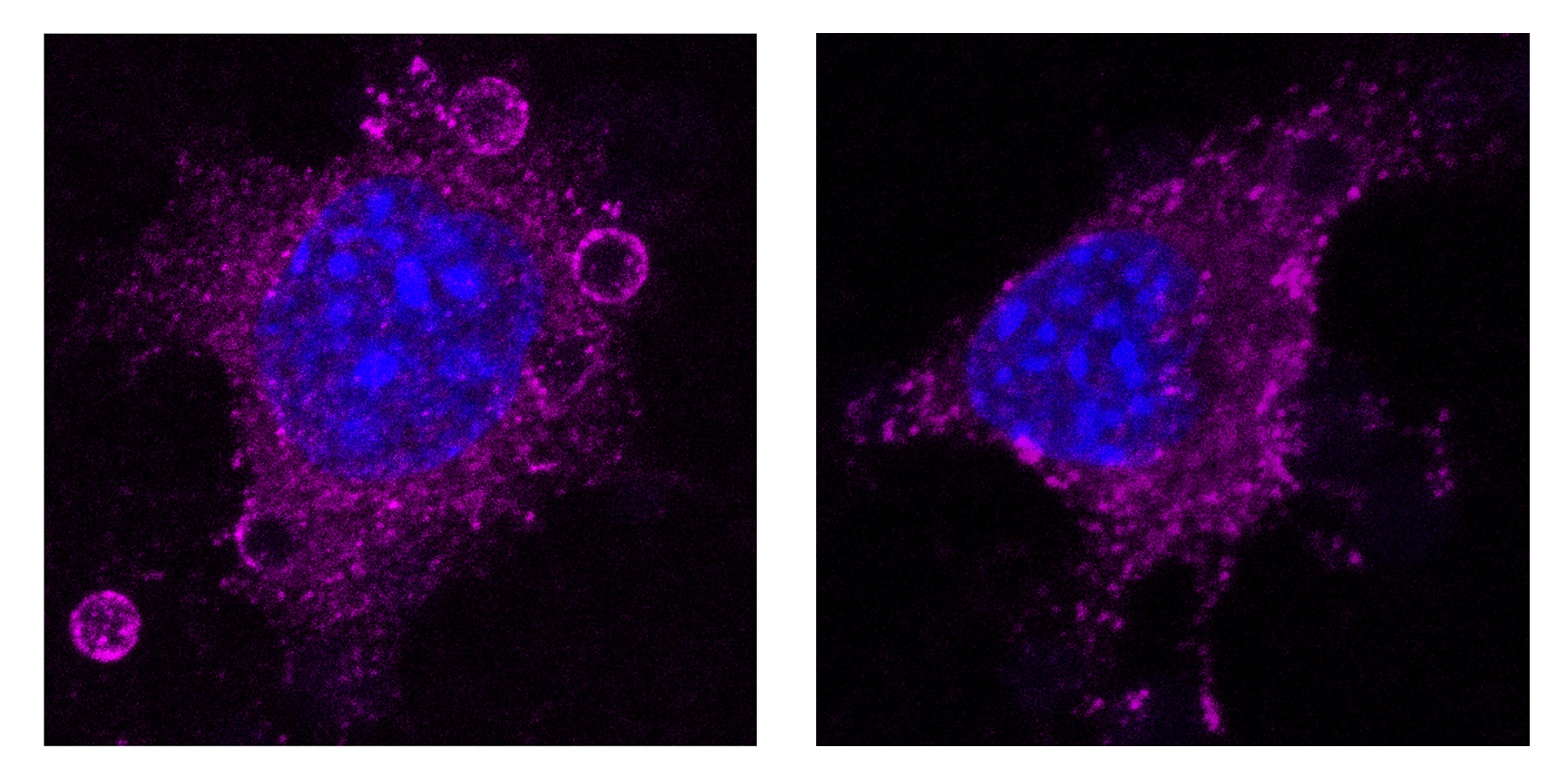
Research 3 Feb 2023 The discovery, published in the journal Immunity, identifies a new therapeutic route for conditions associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, including cardiovascular disease |
|
Research 16 Jan 2023 Nature Cardiovascular Research: The 'guardian of the genome' protects against cardiovascular disease A CNIC study extends the understanding of how acquired mutations in blood cells act as a new cardiovascular risk factor |
|
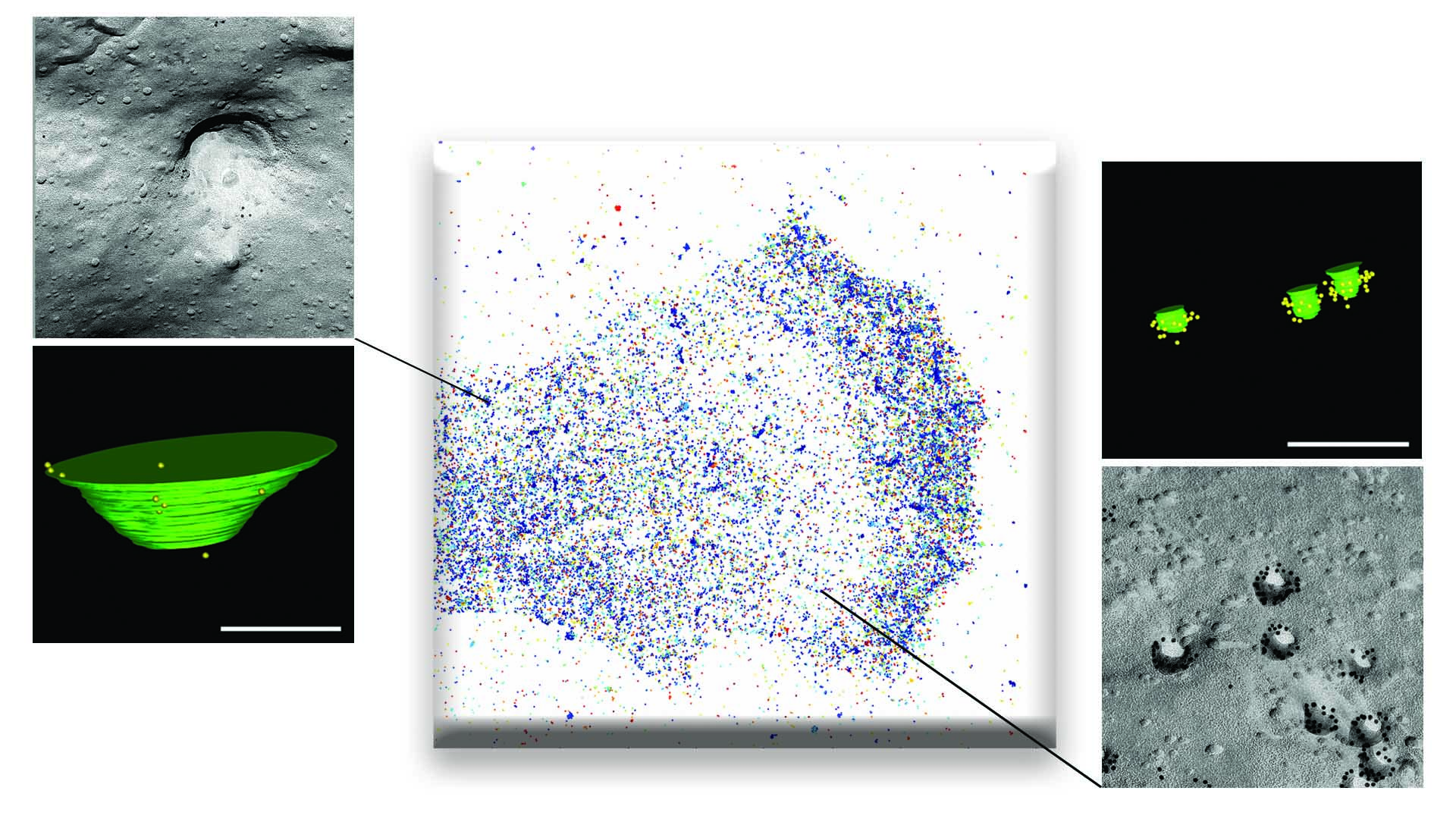
Research 23 Dec 2022 A study published in Nature Cell Biology confirms that caveolae are essential for the mechanical responses of tissues subject to large mechanical forces (such as muscle, heart, blood vessels, and fat), whereas larger membrane depressions (termed 'dolines') are important for the response to weak or medium-strength forces |
|
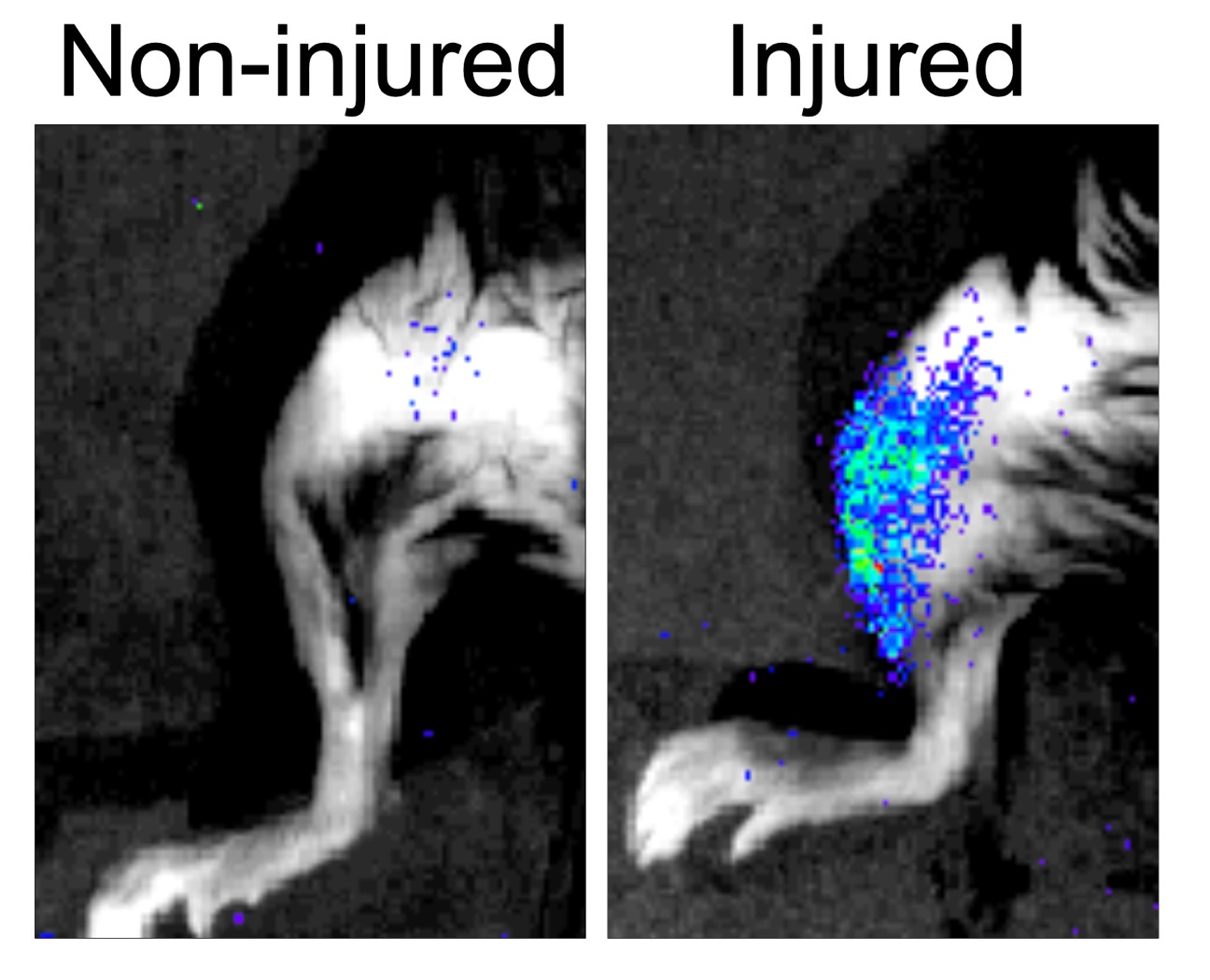
Research 19 Dec 2022 The finding provides a basis for mitigating the loss of muscle regenerative capacity in elderly people and for improving muscle repair in young healthy people |
|
Research 15 Dec 2022 A CNIC team has shown that the retinoid and unsaturated fatty acid sensor RXR is a key protein in the maintenance of a balanced production of the different types of blood cells |
|
Research 13 Dec 2022 A new study published in eLife shows that small cups or nanofolds on the cell membrane called caveolae, by limiting abrupt changes in membrane tension, regulate the number and activity of mechanical microsensors on the cell surface called integrins |
- ‹ previous
- 7 of 49
- next ›