News search
|
About the CNIC 23 Dec 2020 The project will investigate the role of clonal hematopoiesis—the formation of mutated hematopoietic stem-cell clones promoted by anti-cancer therapies—in the development of atherosclerosis and associated cardiovascular disease |
|
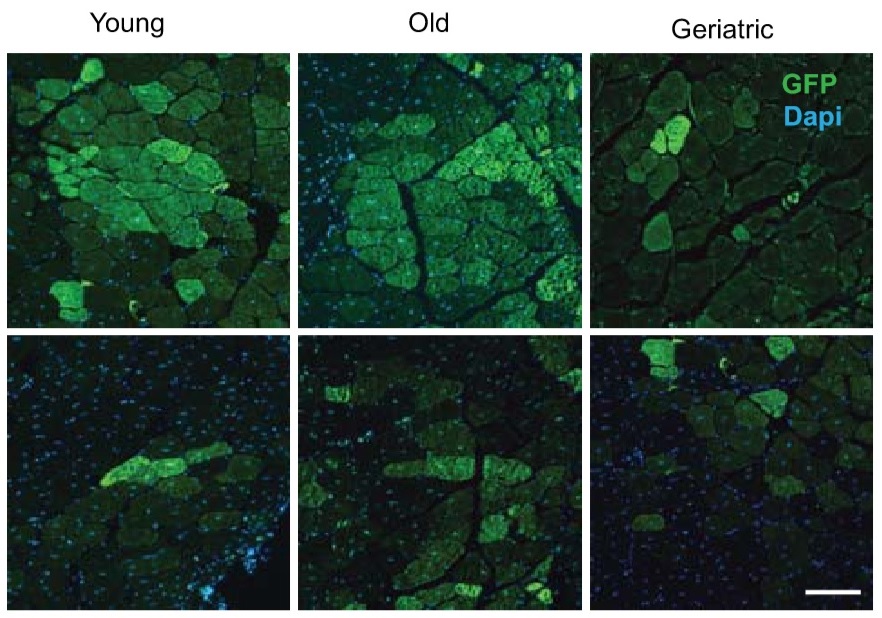
Research 27 Oct 2020 The finding provides a basis for mitigating the loss of muscle regenerative capacity in very elderly people. |
|
Research 22 Oct 2020 CNIC scientists have discovered previously unsuspected actions of the immune system that help to maintain organ health |
|
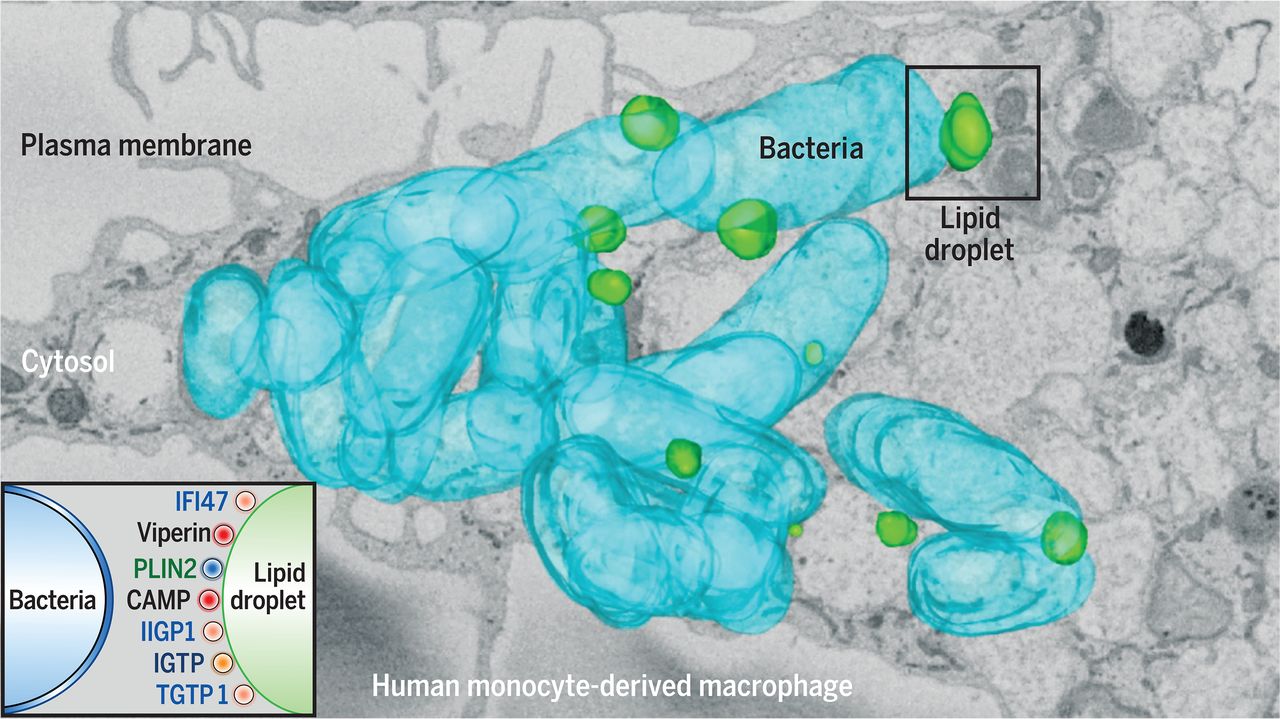
Research 16 Oct 2020 Researchers of IDIBAPS, the University of Barcelona and CNIC describes a new mechanism of innate immunity by which cells fight viruses and bacteria. |
|
Research 17 Sep 2020 The results published in Nature Metabolism could be useful to design new treatments for the obese and overweight, and for some associated pathologies, including fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes |
|
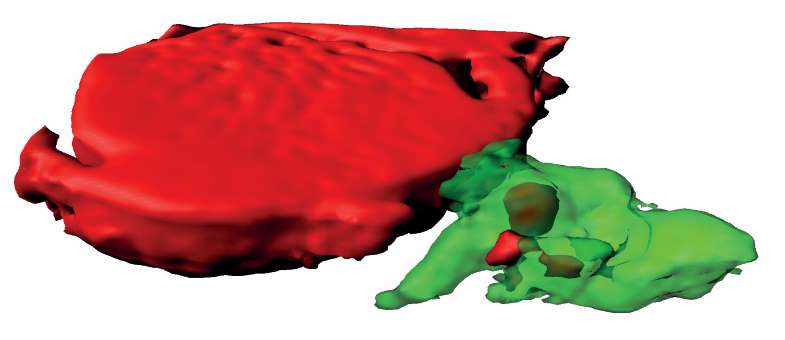
Research 16 Sep 2020 The study published in Cell shows that macrophages, a type of immune cell, help cardiac cells to get rid of their waste material, and that this maintains the metabolic and contractile properties of the heart |
|
Research 30 Jul 2020 CNIC study shows that selection between mitochondrial genomes depends on how each type of mitochondria affects cell metabolism |
|
Research 29 May 2020 The researcher Alejandro Sánchez Alvarado is one of the greatest experts in the study of the mechanisms involved, cellular and biological, in regeneration in the planaria model |
|
Research 28 Apr 2020 CNIC scientists, working with international partners, have developed a new experimental mouse model that allows them to study how cells sense, interpret, and generate mechanical forces |
|
Research 3 Apr 2020 Published in Nature Communications, the study suggests that it may be possible to regulate the number and activity of these macrophages with drugs that modulate the nuclear receptor RXR |
- ‹ previous
- 4 of 8
- next ›