News search
|
Research 14 Apr 2025 A study led by the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (CNIC), in collaboration with the Instituto de Investigación Biomédica de Barcelona (IRB Barcelona), has identified the most effective subtype of dendritic cell for generating immune memory in response to cancer |
|
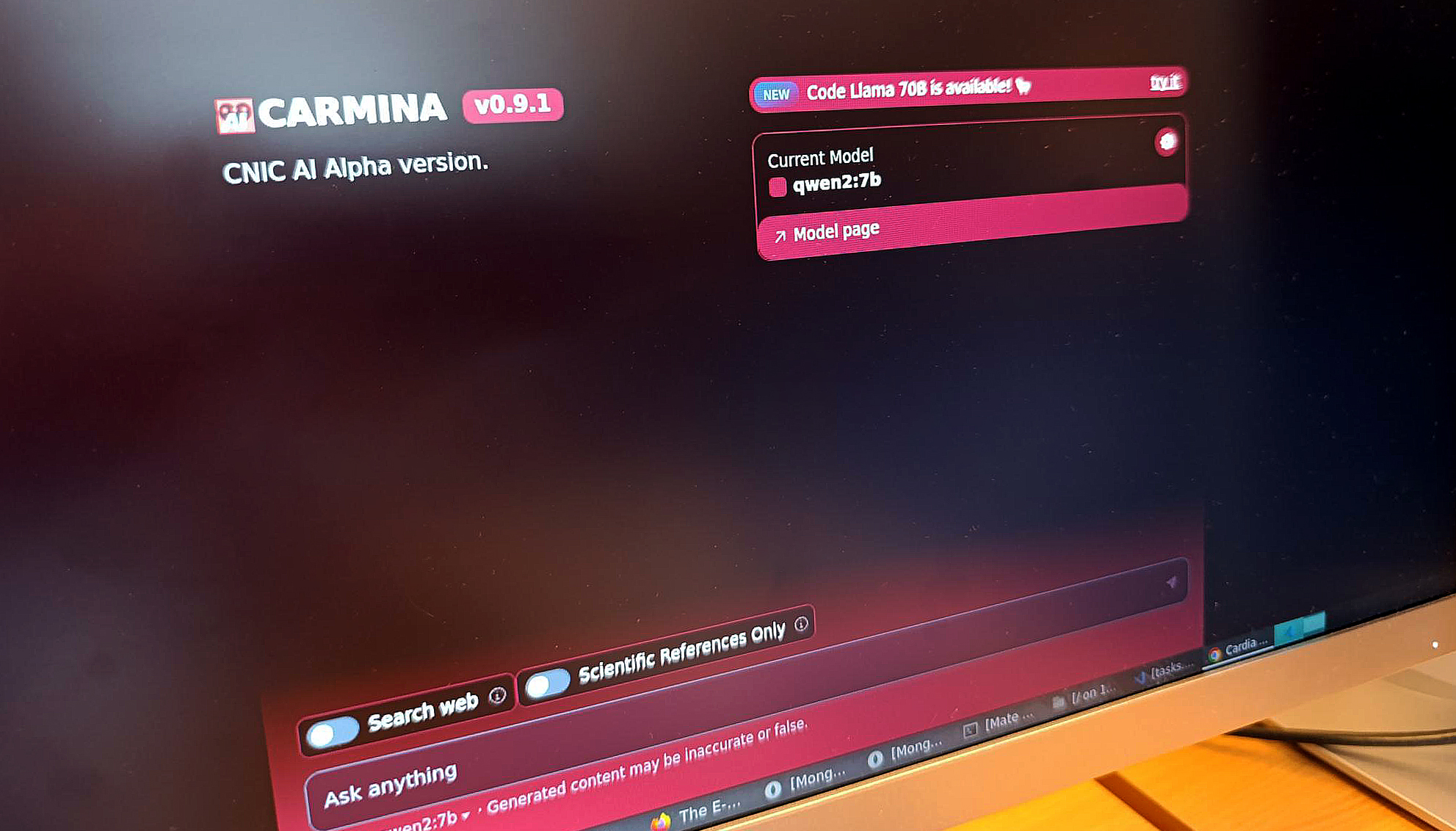
About the CNIC 8 Apr 2025 The system provides specialised answers to biomedical questions, ensuring data privacy by operating exclusively within the CNIC |
|
Research 2 Apr 2025 Scientists at the CNIC and the University of Bern have found that heart surgery in male mice early in life creates a "memory" passed down to the next generation. Published in Circulation, the study suggests that a parental history of heart surgery should be considered when evaluating cardiovascular health in descendants. |
|
Research 31 Mar 2025 The DapaTAVI study, conducted in 39 Spanish hospitals and coordinated by the CNIC, marks a breakthrough in cardiovascular research and could transform the treatment of these patients |
|
About the CNIC 26 Mar 2025 Prof. Yasuyuki Fujita, PhD, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Department of Molecular Oncology |
|
About the CNIC 18 Mar 2025 The CNIC has been allocated €405,625 for its involvement in GRACE, a project focused on developing innovative strategies to improve the detection and management of cardiovascular diseases. |
|
Research 11 Mar 2025 Isabel Gonçalves is a professor and senior consultant at the University of Lun (Sweden). Her research focuses on cardiovascular disease and diabetes. She is the principal investigator in EXODIAB (Excellence in Diabetes Research in Sweden), leads a team at Cardiovascular Research - Translational Studies, and is a researcher in EpiHealth, a project focused on epidemiology for health. |
|
About the CNIC 6 Feb 2025 The accreditation confirms the reliability of the units’ technical output and facilitates external collaborations, factors crucial to sustaining the CNIC’s leadership in cardiovascular research |
|
About the CNIC 19 Dec 2024 The findings of this study have been key for the development of REACT, a new research project, that will count on the collaboration of Santander Bank, and will expand the study of the age group for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, which will include 8,000 new participants. |
- 1 of 16
- next ›